Calculating and reporting VAT on goods imports
VAT-registered enterprises must calculate import VAT themselves and enter the amounts under specific items in the VAT return.
This applies to all purchases of goods, both goods for use in the enterprise and goods for resale. This also applies to goods for which you do not have a deduction entitlement.
When you submit the VAT return in the new format, you must use VAT codes. See an overview of which VAT codes will correspond to the items from the old VAT return.
Private individual or non-VAT registered enterprise?
If you're a private individual or an enterprise that is not registered for VAT, you must make a payment to Norwegian Customs when you import goods into the country or to your shipping agent/haulier when they import goods on your behalf. This wizard is not relevant for you.
What to do:
When you purchase goods from abroad, a customs declaration must be completed. If the goods are sent via a shipping agent, the agent will complete the declaration. Alternatively, you can complete it yourself.
Check that the customs declaration is correct. The information concerning value, transport costs, insurance, etc. must correspond with information on invoices that you receive from the supplier of the goods, the shipping agent or others.
If you discover any errors, you should contact the party responsible and ask them to amend the customs declaration.
The invoice date determines the period under which purchases should be posted. There is also a shipping date, which is the date on which Norwegian Customs registers the goods as arriving in the country. The shipping date determines the period under which the import should be declared in the VAT return.
In some cases, the invoice date and shipping date will fall under different periods. In these cases, the purchase must be posted according to the invoice date, and then declared in the VAT return under the period in which the shipping date falls.
Remember to keep the customs declaration. You will need it when you calculate import VAT. It also constitutes important documentation for bookkeeping purposes.
If you receive goods which you then have to return, e.g. because they were damaged upon arrival, you must treat this in the same way as any other import. You must include goods that are to be returned under total imports. You will normally be entitled to a full deduction entitlement for the purchase in the VAT return.
When you return goods, it is important that you use the procedure code for goods returns, so that the return does not appear to be a sale to another country. There are several procedure codes for the return of goods. You will find the correct procedure code on Norwegian Customs’ website.
Whether goods have been temporarily imported must be stated in the customs declaration. You must reconcile this with the declaration overview. Temporary imports often have a zero rate and must be included under item 85 of the VAT return for periods up to and including 1 January 2022.
If you submit VAT returns for periods up to and including 31 December 2021, you must use the VAT return’s item 11.
If a good changes from temporary import to permanent import, for example, when the good is sold in Norway, the customs declaration must be changed to ordinary import. You can do this by contacting the shipping agent or Norwegian Customs.
If a good is re-imported, this must be included in the customs declaration. You must reconcile this with the declaration overview. Re-import often has a zero rate and must be included under item 85 of the VAT return for periods up to and including 1 January 2022.
If you submit VAT returns for periods up to and including 31 December 2021, you must use the VAT returns item 11.
Do you have all the customs declarations?
You can use the overview sent to you by Norwegian Customs via Altinn to check that you have all the necessary customs declarations.
You must report the VAT under the period in which the shipping date on the customs declaration falls.
When you reconcile the declaration summary against invoices and customs declarations, you will sometimes find errors in the customs declarations. This could for example be:
- Goods are listed that you have not purchased
- Wrong number of goods
- Wrong quantity for goods
- Wrong tax rate
- Wrong goods code
If you find any errors when you reconcile the declaration summary, you must contact the shipping agent or Norwegian Customs so that they can correct the customs declarations which form the basis for the declaration summary. If the shipping agent or Norwegian Customs corrects the errors, the declaration summary will be re-calculated. Remember that the invoice date determines the period under which purchases should be posted.
In other cases, you may find that the declaration summary is correct, but that you are missing certain documents in order for the accounts to be correct. If so, you must contact the supplier or shipping agent and ask them to send you the documentation you need in order to prepare the accounts correctly.
In the VAT return, you must only report purchases from abroad that are present in your accounts and that have been reconciled against the declaration summary. If you are unable to obtain the background information you need to correctly register an import under the current VAT period, you must change this when you finally receive the documentation you need.
In the declaration summary from Norwegian Customs, re-calculations will also be shown. You should note that these can concern previous periods, which should then not be included in the VAT return for the current period.
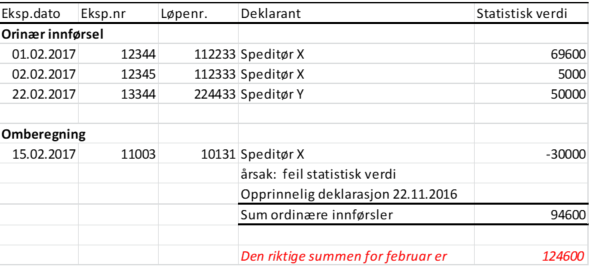
- Does your organisation number have associated businesses (BEDR) in the Register of Legal Entities? One declaration summary for each BEDR will be sent to the parent enterprise’s message box in Altinn.
- Does your organisation number have associated organisational links (ORGL) in the Register of Legal Entities? A declaration summary will be sent to each individual ORGL’s message box in Altinn.
Jointly registered enterprises must check all their organisation numbers.
When the declarations overview has been reconciled with the financial statements, you’re ready to calculate the amounts that must be filled in the VAT return. You use the VAT codes under «Purchases of goods from abroad (import)» if you’re submitting for periods from and including 1 January 2022 and the items «Goods imports» if you submit a VAT return for periods from and including 31 December 2021.
The basis for calculating import VAT is the sum of the statistical value + customs duties and taxes:
Statistical value
By ‘statistical value’, we mean the collective value of the import which Statistics Norway has stipulated is to be stated on the customs declaration. This value is the sum of a number of values in the import.
The statistical value is shown under item 46 of the customs declaration and is the value of the import in Norwegian kroner.
There are some exceptions from the general rule that the VAT basis = statistical value + customs and other duties. This applies for example to imports of artworks, dental work and re-import after having undergone repair, process or adaptation. Read more about the exceptions in the VAT guide (in Norwegian only).
In the customs declaration, these have specific procedure codes under heading 37. There are also other rules which affect the customs value.
Norwegian Customs can provide more information concerning customs values.
Customs and other duties
You'll find customs duty and other taxes such as excise duty, research tax, etc. under item 47 of the customs declaration.
Other duties may include:
- Excise duty, if it's specified in the customs declaration
- Research tax
You should add up all duty and tax shown under item 47. You must add this total to the statistical value in order to obtain the VAT basis.
Find customs duty and other duties
|
Example |
Total |
|
Customs duty |
NOK 1,000 |
|
Excise duties |
NOK 500 |
|
Research tax |
NOK 200 |
|
The total you should add to the statistical value |
NOK 1,700 |
|
|
|
Add customs value and customs duty and other taxes
|
|
Example |
Total |
|
|
Statistical value |
NOK 3,000 |
|
+ |
Customs and other duties |
NOK 1,700 |
|
= |
VAT basis |
NOK 4,700
|
You've now determined the basis for VAT. You should use this amount in order to apply the correct rate and calculate the VAT.
Find VAT
|
|
Example |
Total |
|
|
VAT basis |
NOK 4,700 |
|
* |
VAT rate |
25 % |
|
= |
VAT |
NOK 1,175 |
In the VAT return for periods from and including 1 January 2022, there are five codes relating to import VAT on goods:
- Code 81 – Purchases of deductible goods from abroad (high rate) (also applies to proportional deductibility)
- Code 82 – Purchases of goods from abroad without deduction entitlement (high rate)
- Code 83 – Purchases of deductible goods from abroad (medium rate) (also applies to proportional deductibility)
- Code 84 – Purchases of goods from abroad without deduction entitlement (medium rate)
- Code 85 – Purchases of goods from abroad on which value added tax is not to be calculated (zero rate)
If you’re submitting the VAT return for periods up to and including 31 December 2021, there are three items relating to import VAT on goods:
- Item 9 Sale of goods and calculated VAT 25%
- Item 10 Sale of goods and calculated VAT 15%
- Item 11 Import of goods on which value added tax is not to be calculated
Under item 11, you enter the basis for the VAT but you do not calculate VAT on it.
If you’re entitled to deductions for the import VAT, you must enter this under item 17 and 18.
Read more about the VAT return
Whether goods have been temporarily imported must be stated in the customs declaration. You must reconcile this with the declaration overview. Temporary imports often have a zero rate and must be included under item 85 of the VAT return for periods from and including 1 January 2022.
If you submit VAT returns for periods up to and including 31 December 2021, you must use the VAT return’s item 11.
You can read more about temporary imports on the Norwegian Customs' website.
If a good changes from temporary import to permanent import, for example, when the good is sold in Norway, the customs declaration must be changed to ordinary import. You can do this by contacting the shipping agent or Norwegian Customs.
Whether goods have been temporarily imported must be stated in the customs declaration. You must reconcile this with the declaration overview. Temporary imports often have a zero rate and must be included under item 85 of the VAT return for periods from and including 1 January 2022.
If you submit VAT returns for periods up to and including 31 December 2021, you must use the VAT return’s item 11.
You can read more about re-imports on the Norwegian Customs' website.
You must post the VAT basis that you calculated in the accounts, so that you can report it in the VAT return.
You can post this on a separate account with an offset account, so that it's cancelled out in your accounts. You can also post the VAT basis as debit and credit on a result account under a VAT code.
You must recognise import VAT in the balance sheet. You need separate balance accounts for this, as it must be specified in the VAT return.
You can post on either an ongoing basis or collectively per month. You must document the calculation of the basis and the duty for each VAT rate per customs declaration.
In order to know which account you should post it on, you must know
- whichVAT rate applies to the purchase
- whether you're entitled to deductions for VAT
Accounting
If you have an accounting system, make sure that it's updated with new VAT codes and accounts.
If you do not have an accounting system, you must create the necessary accounts in your accounts. Use the tax return for VAT as an example of how you specify the VAT basis and the tax.
Deduction entitlement
The same rules apply to deductions for purchases from abroad as for purchases of goods and services in Norway.
You must document the following:
- The customs declaration and subvouchers. This is the main part of the documentation. In the case of goods on which VAT is not to be levied, the customs declaration and subvouchers will constitute sufficient documentation.
- The basis for calculating value added tax and the VAT itself. You must document the calculated basis for VAT when importing goods, as well as the calculated VAT. This documentation must show the basis and tax per tax rate for each customs declaration.
Incoming goods invoices are not required to refer to vouchers for import VAT in the accounts. Nor is it a requirement that incoming goods invoices must refer to the customs declaration, but you must be able to document this.
Relevant links
- Bookkeeping Regulation(Lovdata).
- Statement concerning good bookkeeping practice (GBS9) - Itemisation of the basis for input VAT in connection with imports of goods and documentation and retention requirements(the Norwegian Accounting Standards Board) (in Norwegian only).
The text concerning bookkeeping presents a brief review of the rules that were introduced in 2017. You can download more detailed information here (PDF).